 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeAn element with density 2.8 g cm−3 forms of the f.c.c. unit cell with edge length 4 X10−8 cm. Calculate the molar mass of the element.
(Given: NA = 6.022 X 1023 mol −1)
(i) What type of non-stoichiometric point defect is responsible for the pink colour of LiCl?
(ii) What type of stoichiometric defect is shown by NaCl?
OR
How will you distinguish between the following pairs of terms:
(i) Tetrahedral and octahedral voids
(ii) Crystal lattice and unit cell.
An element has atomic mass 93 g mol–1 and density 11.5 g cm–3. If the edge
the length of its unit cell is 300 pm, identify the type of unit cell.
Given,
M= 93 g mol-1
d= 11.5 g cm-3
a = 300 pm = 300 x 10-10 cm = 3 x 10-8
We know that,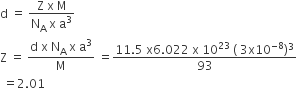
The number of atoms present in given unit cells is coming nearly equal to 2. Hence, the given unit cell is body centered cubic unit cell (BCC).
Calculate the number of unit cells in 8.1 g of aluminium if it crystallizes in a
f.c.c. structure. (Atomic mass of Al = 27 g mol–1)
Give reasons :
In stoichiometric defects, NaCl exhibits Schottky defect and not Frenkel
defect.
Give reason:
Ferrimagnetic substances show better magnetism than antiferromagnetic
substances.
Analysis shows that FeO has a non-stoichiometric composition with formula Fe0.95O. Give reason.
An element ‘X’ (At. mass = 40 g mol–1) having f.c.c. the structure has a unit cell edge length of 400 pm. Calculate the density of ‘X’ and the number of unit cells in 4 g of ‘X’. (NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol–1 )
