 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsCarbon cannot reduce Fe2O3 to Fe at a temperature below 983 K because
free energy change for the formation of CO is more negative than that of Fe2O3
CO is thermodynamically more stable than Fe2O3
carbon has higher affinity towards oxygen than iron
iron has higher affinity towards oxygen than carbon
D.
iron has higher affinity towards oxygen than carbon
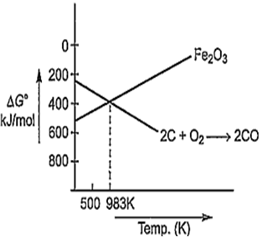
Below 983 K, conversion of iron to ferric oxide is more favourable.
The percentage of p-character of the hybrid orbitals in graphite and diamond are respectively
50 and 75
67 and 75
33 and 75
33 and 25
An alkali metal hydride (NaH) reacts with diborane in. A to give a tetrahedral compound B which is extensively used as reducing agent in organic synthesis. The compounds A and B respectively are
C2H6 and C2H5Na
CH3COCH3 and B3N3H6
C6H6 and NaBH4
(C2H5)2O and NaBH4
The correct statement is
BF3 is the strongest Lewis acid among the other boron halides
BI3 is the weakest Lewis acid among the other boron halides
there is maximum pπ- pπ back boinding in BF3
there is minimum pπ- pπ back boinding in BF3
The hybridisation of C in diamond, graphite and ethyne is in the order.
sp3, sp, sp2
sp3, sp2, sp
sp, sp2, sp3
sp2, sp3, sp
The electronegativities of C, N, Si and P are in the order of
P < Si<C < N
Si <P < C<N
P < Si < N < C
Si <P < N <C
Addition of mineral acid to an aqueous solution of borax, the following compound is formed
pyroboric acid
boron hydride
meta boric acid
orthoboric acid
