 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWhat happens when:
(i) sodium metal is dropped in water?
(ii) sodium metal is heated in free supply of air?
(iii) sodium peroxide dissolves in water?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeAccount for the following:
(i) Sodium imparts colour to the flame.
(ii) Sodium acts as a strong reducing agent.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeDiscuss in brief the Solvay process for the manufacture of washing soda.

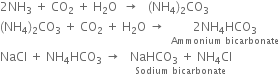

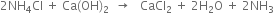
Process. The actual manufacture of sodium carbonate is carried out as follows:
1. Saturating or ammoniation tank. It is an upright iron cylinder having a conical base. The brine solution is taken in this tower and a mixture of ammonia gas and carbon dioxide is bubbled through it. Any impurities of calcium and magnesium salts in the brine solution are precipitated as carbonates and removed with the help of filter press.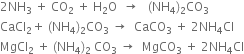
2. Carbonating tower. It is provided with perforated horizontal plates. The clear ammoniacal brine after cooling flows downward slowly and carbon dioxide (from lime kiln) introduced at the base of the tower rises in small bubbles. Ammonical brine and carbon dioxide move in opposite directions and therefore, the two react on the principle of counter currents. Sodium bicarbonate is formed which is least soluble in excess of carbon dioxide and sodium chloride and hence precipitated.
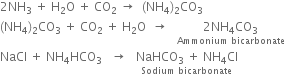
3. Rotary vacuum filter. The milky liquid containing small crystals of sodium bicarbonate is drawn off at the base of the carbonating tower. It is filtered by means of a rotary vacuum filter and then scrapped off. The remaining liquor containing NH4Cl is pumped to the top of the ammonia recovery tower.
4. Calcination of sodium bicarbonate. The sodium bicarbonate is calcined in a covered pan or a rotary furnace. It undergoes decomposition to form sodium carbonate, carbon dioxide and stream.
Carbon dioxide set free is again used in the carbonating tower together with the gas(from lime kiln).
5. Limekiln. Here lime -stone is heated to get carbon dioxide and calcium oxide.

Carbon dioxide formed is passed through the base of carbonating tower to form NaHCO3. The CaO is treated with a large quantity of water to get Ca(OH)2 which is pumped on to the ammonia recovery tower.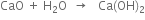
6. Ammonia recovery tower. The filtrate from the vacuum filter (Step 3) containing ammonium chloride is heated (using steam) along with Ca(OH)2 (obtained from lime kiln) to get a mixture of ammonia with a small amount of carbon dioxide gas. 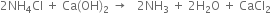
The ammonia with a small amount of carbon dioxide evolved is returned to the saturating tank for re-use. CaCl2 is the only waste product of this process.
Thus, the ammonia-soda process is very cheap, self-contained and self-sufficient and sodium carbonate formed is quite pure.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type