 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeBeryllium and magnesium do not give colour to flame whereas other alkaline earth metals do so. Why?
Comment on each of the following observations: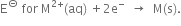
(where M = Ca, Sr or Ba) is nearly constant.
Explain why alkaline earth metals are poor reducing agents as compared to alkali metals.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeExplain the trend of solubility of carbonate, sulphates and hydroxides of alkaline earth metals ?
The solubility of carbonates and sulphates of these metals decreases downward in the group. This is because the magnitude of the lattice enthalpy remains almost constant as the carbonate or sulphate is so big that small increase in the size of the cations from Be to Ba does not make any difference. However, the hydration enthalpy decreases from Be2+ to Ba2+ sufficiently with the increase in their size resulting in the decrease of solubility of their carbonates or sulphates.
The solubility of hydroxides of these metals in water increases downward in the group. This is due to the fact that the lattice enthalpy decreases down the group due to increase in the size of the cation of the alkaline earth metal. On the other hand, the hydration enthalpy of the cations of alkaline earth metals decreases as we go down the group. As a result ∆Hsolution (∆Hlattice – ∆Hhydration) becomes more negative and solubility increases.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeAccount for the following:
(i) Be(OH)2 is amphoteric while Mg(OH)2 is basic.
(ii) Be(OH)2 is insoluble but Ba(OH)2 is fairly soluble in water.
