 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhat are the types of systems?
Types of systems. The exchange of energy between the system and its surroundings usually takes place in the form of heat or work or both. Based upon this, the systems have been classified into three types:
(i) Open system (ii) Closed system (iii) Isolated system.
(i) Open system: A system is said to be an open system if it exchanges the matter (mass) as well as the energy with its surroundings. All chemical reactions carried in open containers constitute the open system. For example,
(a) Combustion of carbon in an open tube.
(b) Tea placed in a cup.
(ii) Closed system: A system is said to be a closed system if the only exchange of energy is possible between system and surroundings and exchange of matter (mass) is not possible. All chemical reactions carried in closed containers constitute closed system e.g.
(a) Decomposition of calcium carbonate in a closed tube.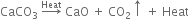
(b) Tea placed in a tea-pot.
(iii) Isolated system: A system which can neither exchange energy nor matter (mass) with its surroundings is called an isolated system. All chemical reactions carried in a closed container insulated from all sides represent the isolated system. For example.
(a) Neutralisation reaction between NaOH and HCl carried in a thermos flask.
(b) Tea placed in a thermos flask.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWhat do you understand by:
(i) Isothermal process
(ii) Adiabatic process
(iii) Isobaric process
(iv) Isochoric process
(v) Cyclic process?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeClassify the following processes as reversible or irreversible:
(i) mixing of two gases by diffusion.
(ii) dissolution of sodium chloride in water
(iii) evaporation of water at 373 K at 1 atm pressure
(iv) expansion of a gas in vacuum.
