 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeThe enthalpy change (∆H) for the reaction
![]()
is -92.38 kJ at 298 K. what is the ![]() at 298 K?
at 298 K?
∆U⊝ of combustion of methane is –X kJ mol–1. The value of ∆H⊝ is :
(i) = ∆U⊝
(ii) > ∆U⊝
(iii) < ∆U⊝
(iv) = 0
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhat do you understand by:
(i) Heat capacity of a substance
(ii) Heat capacity at constant volume
(iii) Heat capacity at constant pressure?
60.8 J of energy is required to change the temperature of 25.0 g of ethylene glycol (a compound used as an antifreeze in automobile engines) by 1.0 K. Calculate heat capacity of ethylene glycol.
We know,
 ...(1)
...(1)
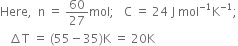
Substituting the values in eq. (1), we get

= 1066.7 J = 1.07 kJ
