 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeCalculate the heat change accompanying the transformation of C(graphite) to C(diamond). You are given:

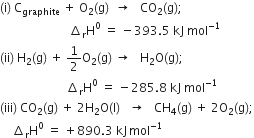
The combustion of one mole of benzne takes place at 298K and 1 atm. After combustion, CO2(g) and H2O (l) are produced and 3267.0 kJ of heat is liberated. Calculate the standard enthalpy of formation, ∆fH° of benzene. Standard enthalpies of formation of CO2(g) and H2O(l) are – 393.5 kJ mol–1 and –285.83 kJ mor–1respectively.
What do you mean by bond enthalpy? When is bond enthalpy equal to bond dissociation energy?
Chemical reactions involve the breaking and making of chemical bonds. Energy is required to break a bond and energy is released when a bond is formed. The bond enthalpy is the amount of energy necessary to break bonds in one mole of a gaseous covalent substance to form products in the gaseous state. The bond enthalpy for H2 is 435.0 kJ mol–1.
This endothermic reaction (∆H0 is positive) can be written as,
Bond energy of a diatomic molecule (e.g. H2, Cl2, O2 etc.) is equal to its dissociation energy. The dissociation energy of a bond is defined as the enthalpy change involved in breaking the bond between atoms of a gaseous homonuclear molecule.
Calculation of enthalpy of reaction from bond energies: We know that when a reaction takes place, some bonds are broken while some new bonds are formed. Energy is required to the dissociation of bonds while energy is released when the bonds are formed.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type