 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeProve that in a reversible process:
∆(system) + ∆S(surroundings) = 0
Or
Prove that there is no net change in entropy in a reversible process.
Suppose heat is absorbed by the system reversible and the heat is lost by the surroundings also reversibly (process occurs under complete reversible condition).
If qrev is the heat absorbed by the system reversibly, then the heat lost by the surroundings will also be qrev. If the process takes place isothermally at T kelvin, then Entropy change of the system
Entropy change of the surroundings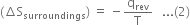
Hence the total entropy change for the combined system and surroundings will be: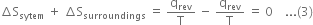
Hence in a reversible process, the net entropy change for the combined system and the surroundings is zero i.e. there is no net change in entropy.
What do you understand by:
(i) The entropy of fusion?
(ii) The entropy of vapourisation ?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeYou are given normal boiling points and standard enthalpies of vapourisation. Calculate the entropy of vapourisation of liquids listed below:
Liquid 

Calculate the entropy change of n-hexane when 1 mole of it evaporates at 341.7 K(∆Hvap = 29.0 kJ mol–1).
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWhat are the two tendencies which determine the feasibility of process? How are the two related to each other?
