 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeExplain Gibb's Helmholtz equation.
Gibbs-Helmholtz equation is
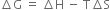
The value of ∆G can be zero, positive or negative.
(i) If ∆G = 0, the reaction is in the state of equilibrium i.e. ∆H = T∆S.
(ii) If ∆G = – ve, the reaction is spontaneous in the forward direction.
(iii) If ∆G = +ve, the reaction is non-spontaneous i.e. reaction is spontaneous in the reverse direction.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWhat is free energy change? Show that the change in free energy is equal to useful work done.
or
prove that –∆G = w(useful work)
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypePredict the enthalpy change, free energy change and entropy change when ammonium chloride is dissolved in water and the solution becomes colder.
At ![]() , ice and water are in equilibrium and
, ice and water are in equilibrium and ![]() for the process
for the process ![]() Calculate
Calculate ![]() for the conversion of ice to liquid water.
for the conversion of ice to liquid water.
For the reaction![]()
calculate ![]() at 700K when enthalpy and entropy changes are -113 kJ mol-1 and -145 JK-1 mol-1 respectively.
at 700K when enthalpy and entropy changes are -113 kJ mol-1 and -145 JK-1 mol-1 respectively.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeFrom the following values of ∆H and ∆S, decide whether or not these reactions will be spontaneous at 298 K:
Reaction A:
∆H = – 10.5 X 103 J mol–1
∆S = + 31 JK–1 mol–1
Reaction B:
∆H = – 11.7 X 103 J mol–1 ;
∆S = –105 jK–1 mol–1.
