 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWhat is free energy change? Show that the change in free energy is equal to useful work done.
or
prove that –∆G = w(useful work)
(i) The overall criterion of a process to occur spontaneously i.e. driving force is expressed in terms of free energy change (∆G).
Free energy change (∆G) is related to enthalpy change (∆H) and entropy change (∆S) as ∆G = ∆H – T∆S [Gibbs-Helmoltz equation] For a spontaneous process, ∆G should have negative value.
(ii) According to first law of thermodynamics,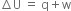
where q is heat absorbed by the system. ∆U is the change in internal energy and w is the work done on the system.
If we are to determine the work a system can do, then w should be taken as – w.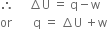
Now w includes expansion as well as non-expansion work. 
But work due to expansion at constant temperature is given by P∆V.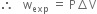
wnon-exp is also called useful work because this type of work can be used for useful effect e.g. electrical work.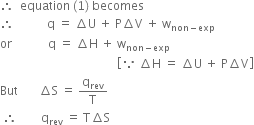
Substituting this value in (2), we have,

or 

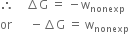
This means that decrease in free energy of a system (–∆G) is a measure of the non-expansion or useful work done by the system in a process or –∆G = wuseful work
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypePredict the enthalpy change, free energy change and entropy change when ammonium chloride is dissolved in water and the solution becomes colder.
At ![]() , ice and water are in equilibrium and
, ice and water are in equilibrium and ![]() for the process
for the process ![]() Calculate
Calculate ![]() for the conversion of ice to liquid water.
for the conversion of ice to liquid water.
For the reaction![]()
calculate ![]() at 700K when enthalpy and entropy changes are -113 kJ mol-1 and -145 JK-1 mol-1 respectively.
at 700K when enthalpy and entropy changes are -113 kJ mol-1 and -145 JK-1 mol-1 respectively.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeFrom the following values of ∆H and ∆S, decide whether or not these reactions will be spontaneous at 298 K:
Reaction A:
∆H = – 10.5 X 103 J mol–1
∆S = + 31 JK–1 mol–1
Reaction B:
∆H = – 11.7 X 103 J mol–1 ;
∆S = –105 jK–1 mol–1.
