 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeThe length x of a rectangle is decreasing at the rate of 3 cm/minute and the width y is increasing at the rate of 2 cm/minute. When x = 10 cm and y = 6 cm, find the rate of change of (a) the perimeter and (b) the area of rectangle
The length x of a rectangle is decreasing at the rate of 5 cm/minute and the width y is increasing at the rate of 4 cm/minutc. When x = 8 cm and y = 6 cm, find the rates of change of (a) the perimeter, and (b) the area of the rectangle.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeThe two equal sides of an isosceles triangle with fixed base b are decreasing at the rate of 3 cm per second. How fast is the area decreasing when the two equal sides are equal to the base?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeA particle moves along the curve 6y = x3 + 2. Find the points on the curve at which the y-coordinate is changing 8 times as fast as the x-coordinate.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeAt what points of the ellipse 16x2 + 9y2 = 400, does the ordinate decrease at the same rate at which the abscissa increases?
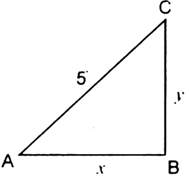
A ladder 5 m long is leaning against a wall. The bottom of the ladder is pulled along the ground, away from the wall, at the rate of 2 cm/s. How fast is its height on the wall decreasing when the foot of the ladder is 4m away from the wall?
Let the foot A of the ladder be at a distance x metres from the wall and y metres be the height of the wall at any time t.
![]()
Differentiating both sides w.r.t. 't', we get,
![]()
![]()
![]() (given)
(given)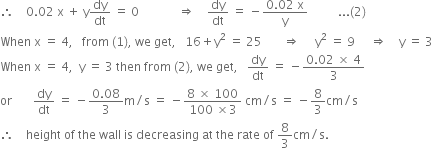
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeSand is pouring from a pipe at the rate of 12 cm3/s. The falling sand forms a cone on the ground in such a way what the height of the cone is always one-sixth of the radius of the base. How fast is the height of the sand-cone increasing when the height is 4 cm?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeA man 2 metres high walks at a uniform speed of 6 metre/sec away from a lamp-post 6 metres high. Find the rate at which the length of his shadow increases.
A man of height 2 metres walks at a uniform speed of 5 km/h away from a lamp post which is 6 metres high. Find the rate at which the length of his shadow increases.
