 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice Questions0
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeUsing the method of integration, find the area of the triangular region whose vertices are (2, -2), (4, 3) and (1, 2).
Sketch the region bounded by the curves  and find its area using integration.
and find its area using integration.
Consider the given equation. 
This equation represents a semicircle with centre at the origin and radius = 
Given that the region is bounded by the above semicircle and the line 
Let us find the point of intersection of the given curve meets the line 
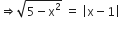
Squaring both the sides, we have,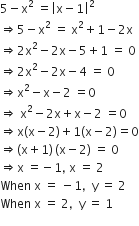
Consider the following figure
Thus the intersection points are 1,2 and 2,1 ( ) ( ) Consider the following sketch of the bounded region.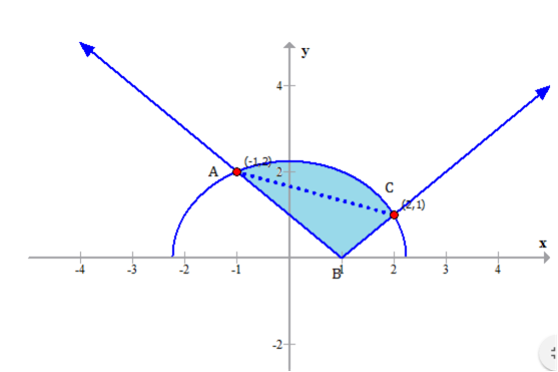
Required Area, 

Using integration, find the area of the region bounded by the triangle whose vertices are (-1, 2), (1, 5) and (3, 4).
Using integration, find the area bounded by the curve x2 = 4y and the line x = 4y – 2.
