Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeIn Fig. 12.30, OACB is a quadrant of a circle with centre O and radius 3.5 cm. If OD = 2 cm, find the area of the (i) quadrant OACB, (ii) shaded region. 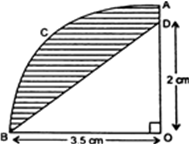
In Fig. 12.31, a square OABC is inscribed in a quadrant OPBQ. If OA = 20 cm, find the area of the shaded region. (Use ŌÄ = 3.14).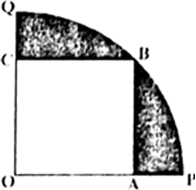
Fig. 12.31
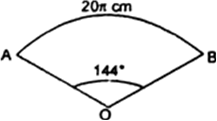
AB and CD are respectively arcs of two concentric circles of radii 21 cm and 7 cm and centre O (see Fig. 12.32). If ‚ą† AOB = 30¬į, find the area of the shaded region.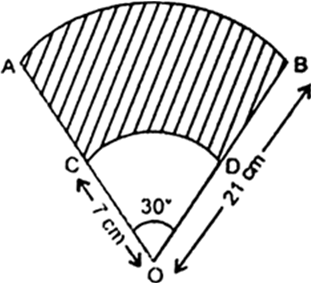
Fig. 12.32
Let r1 = 7 cm (for sector OCDO) and r2 = 21 (for sector OBAO)
r2 (for sector OABO) = 21 cm
and, ¬†¬†¬†”© = 30¬į
Now,  Area of sector (OCDO)
¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬†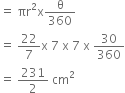
and, Area of sector (OABO)
¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬†¬†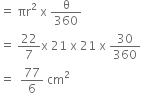
Hence, required area |(shaded part)
         = Area of sector (OCDO) - Area of sector (OABO)
       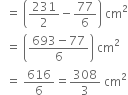
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeIn Fig. 12.33, ABC is a quadrant of a circle of radius 14 cm and a semicircle is drawn with BC as diameter. Find the area of the shaded region. 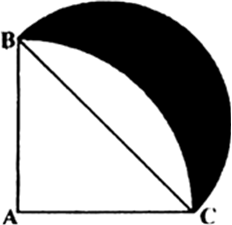
Fig. 12.33
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeCalculate the area of the designed region in Fig. 12.34 common between the two quadrants of circles of radius 8 cm each.
Fig. 12.34