Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice Questions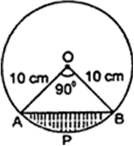
 Short Answer Type
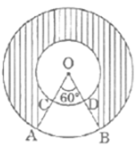
Short Answer TypeIn Fig. find the area of the shaded region, enclosed between two concentric circles of radii 7 cm and 14 cm where ∠AOC = 40°. (use π =22/7)

In the given figure, a triangle ABC is drawn to circumscribe of radius 3 cm, such that the segments RD and DC are respectively of length 6 cm and 9 cm. If the area of ΔABC is 54 cm2, then find lengths of sides AB and AC.
Suppose the given circle touch the sides AB and AC of the triangle at point F and E, respectively. Let the length of the line segment AF is x cm.
We know that the length of tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal.
In ΔABC,
CE = CD = 9 cm (Tangents of the circle from point C)
BF = BD = 6 cm (Tangents on the circle from point B)
AE = AF + FB = x + 6
BC = BD + DC = 6 + 9 = 15
CA = CE + EA = 9 + x
Find the area of the minor segment of a circle of radius 14 cm, when its central angle is 60°. Also find the area of the corresponding major segment. [ use π = 22/7 ]
 Long Answer Type
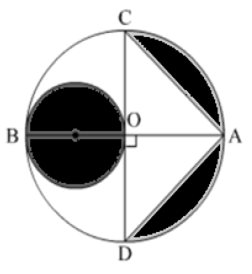
Long Answer TypeIn Fig., AB and CD are two diameters of a circle with centre O, which are perpendicular to each other. OB is the diameter of the smaller circle. If OA = 7 cm, find the area of the shaded region.
In Figure 2, ABCD is a trapezium of area 24.5 sq. cm. In it, AD|| BC, DAB = , AD = 10 cm and BC = 4 cm. If ABE is a quadrant of a circle, find the area of the shaded region.

 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeIn Figure, two concentric circles with centre 0, have radii 21 cm and 42 cm. If ∠ AOB = 60°, find the area of the shaded region.