 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type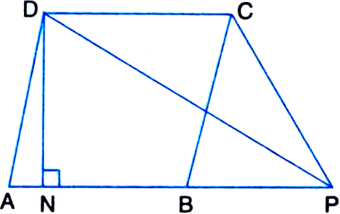
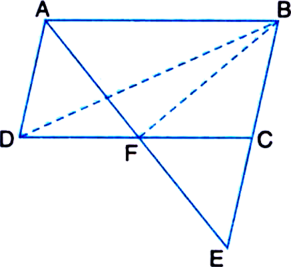
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeD, E and F are respectively the midpoints of the sides BC, CA and AB of a ΔABC. Show that:
(i) BDEF is a parallelogram
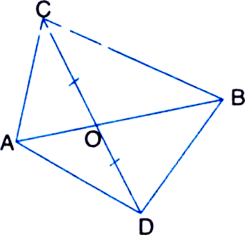
In figure, diagonals AC and BD of quadrilateral ABCD intersect at O such that OB = OD. If AB = CD, then show that:
(i) ar(ΔDOC) = ar(ΔAOB)
(ii) ar(ΔDCB) = ar(ΔACB)
(iii) DA || CB or ABCD is a parallelogram.
[Hint. From D and B, draw perpendiculars to AC.]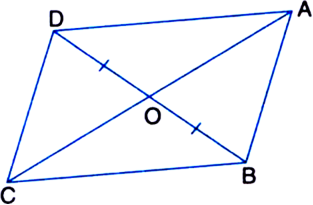
Given: Diagonals AC and BD of a quadrilateral ABCD intersect at O such that OB = OD. To Prove: If AB = CD, then
(i) ar(ΔDOC) = ar(ΔAOB)
(ii) ar(ΔDCB) = ar(ΔACB)
(iii) DA || CB or ABCD is a parallelogram.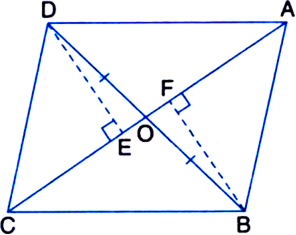
Construction: Draw DE ⊥ AC and BF ⊥ AC.
Proof: (iii) In ΔADB,
∵ AO is a median
∴ ar(ΔAOD) = ar(ΔAOB) ...(1)
∵ A median of a triangle divides it into two triangles of equal areas
In ΔCBD,
∵ CO is a median.
ar(ΔCOD) = ar(ΔCOB) ...(2)
∵ A median of a triangle divides it into two triangles of equal areas
Adding (1) and (2), we get ar(ΔAOD) + ar(ΔCOD)
= ar(ΔAOB) + ar(ΔCOB)
⇒ ar(ΔACD) = ar(ΔACB)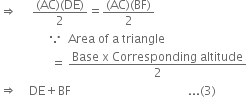
In right Δs DEC and BFA,
Hyp. DC = Hyp. BA | given
DE = BF | From (3)
∴ ΔDEC ⊥ ABFA | R.H.S. Rule
∴ ∠DCE = ∠BAF | C.P.C.T.
But these angles form a pair of equal alternate interior angles.
∴ DC || AB ...(4)
∵ DC = AB and DC || AB ∴ □ABCD is a parallelogram.
∵ A quadrilateral is a parallelogram if a pair of opposite sides are parallel and equal DA || CB
| ∵ Opposite sides of a || gm are parallel (i) ∵ ABCD is a parallelogram
∴ OC = OA ...(5)
Diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other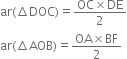
∵ DE = BF | From (3)
and OC = OA | From (5)
∴ ar(ΔDOC) = ar(ΔAOB).
(ii) From (i),
ar(ΔDOC) = ar(ΔAOB)
Δ ar(ΔDOC) + ar(ΔOCB)
= ar(ΔAOB) + ar(ΔOCB)
| Adding equal areas on both sides ⇒ ar(ΔDCB) = ar(ΔACB).
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type