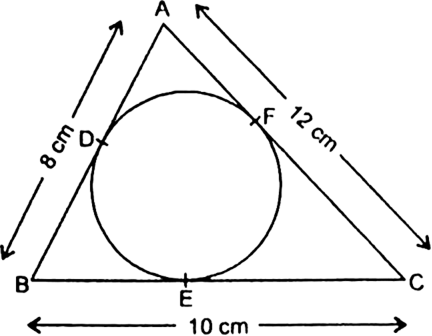
Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type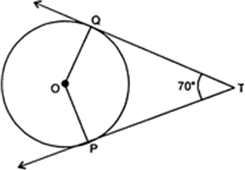
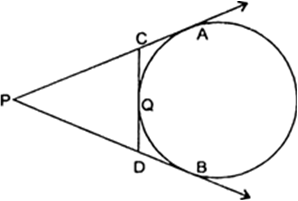



Given : A circle with centre O, an external point P and two tangents PA and PB to the circle, where A and B are points of contact (Fig. 10.36A).
To Prove : ∠APB 2∠OAB
Proof : Let ∠APB = 9 ∴ PA = PB
[∴ Tangents from an ext. pt. are equal]![]()
![]() APB is ab isosceles triangle
APB is ab isosceles triangle

Hence, ∠APB = 2 ∠OAB. Proved.