 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeAB and CD are two parallel chords of a circle, on the same side of the centre. If AB = 12 cm, CD = 24 cm and the distance between the chords is 4 cm, find the radius of the circle.
In the figure, two circles with centres A and B intersect each other at C and D. Prove that ∠ACB = ∠ADB.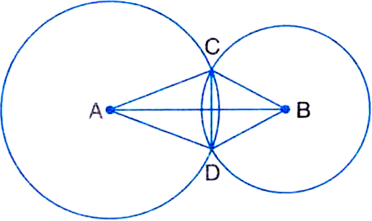
If two equal chords of a circle intersect within the circle, prove that the line joining the point of intersection to the centre makes equal angles with the chords.
If a line intersects two concentric circles (circles with the same centre) with centre O at A, B, C and D, prove that AB = CD (see Fig.)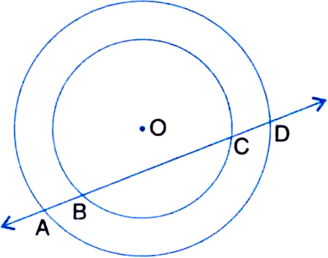
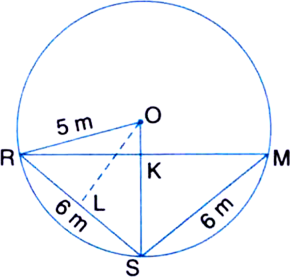
Three girls Reshma, Salma and Mandip are playing a game by standing on a circle of radius 5m drawn in a park. Reshma throws a ball to Salma, Salma to Mandip, Mandip to Reshma. If the distance between Reshma and Salma and between Salma and Mandip is 6m each, what is the distance between Reshma and Mandip?
Let KR = x m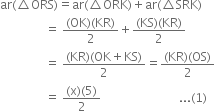
Again, ar (∆ORS)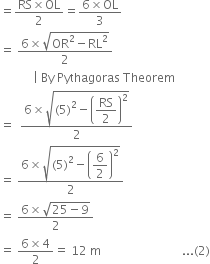
From equations (1) and (2),![]()
⇒ KR = 4.8 m
∴ RM = 2KR = 2 × (4.8) = 9.6 m
Hence, the distance between Reshma and Mandip is 9.6 m.
A circular park of radius 20m is situated in a colony. Three boys Ankur, Syed and David are sitting at equal distance on its boundary each having a toy telephone in his hands to talk each other. Find the length of the string of each phone.
