 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeIn figure A,B and C are three points on a circle with centre O such that ∠ BOC = 30° and ∠ AOB = 60°. If D is a point on the circle other than the arc ABC, find ∠ADC.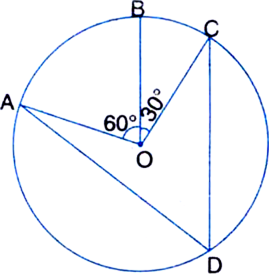
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type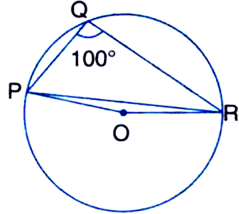
Take a point S in the major arc. Join PS and RS.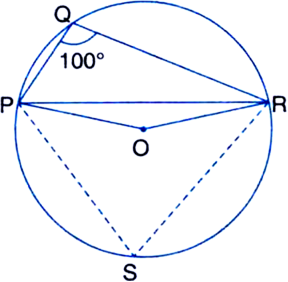
∵ PQRS is a cyclic quadrilateral.
∴ ∠PQR + ∠PSR = 180°
| The sum of either pair of opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral is 180°
⇒ 100° + ∠PSR = 180°
⇒ ∠PSR = 180° - 100°
⇒ ∠PSR = 80° ...(1)
Now, ∠POR = 2∠PSR
| The angle subtended by an arc at the centre is double the angle subtended by it at any point on the remaining part of the circle
= 2 × 80° = 160° ...(2)
I Using (1)
In ∆OPR,
∵ OP = OR | Radii of a circle
∴ ∠OPR = ∠ORP ...(3)
| Angles opposite to equal sides of a triangle are equal
In ∆OPR,
∠OPR + ∠ORP + ∠POR = 180°
| Sum of all the angles of a triangle is 180°
⇒ ∠OPR + ∠OPR + 160° = 180°
| Using (2) and (1)
⇒ 2∠OPR + 160° = 180°
⇒ 2∠OPR = 180° - 160° = 20°
⇒ ∠OPR = 10°.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type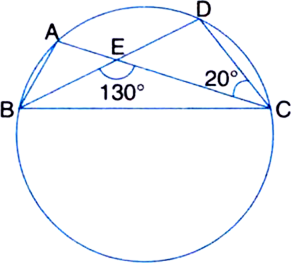
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeIf the non-parallel sides of a trapezium are equal, prove that it is cyclic. Prove that an isosceles trapezium is cyclic.
