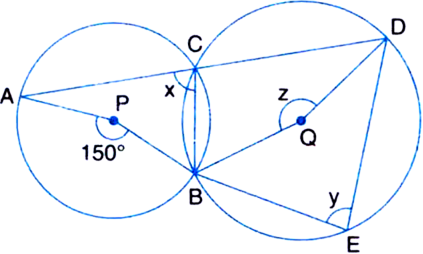
Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type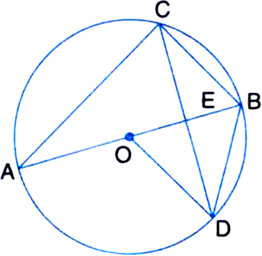
Given: O is the centre of the circle. BD = OD and CD ⊥ AB.
To determine: ∠CAB
Construction: Join OC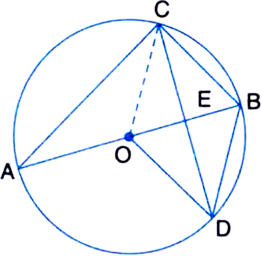
Determination: ∵ BD = OD
∴ ∠DOE = ∠DBE
| Angles opposites to equal sides of a triangle are equal
In ∆OED and ∆BED,
∠DOE = ∠DBE | From above
∠DEO = ∠DEB
| Each = 90° (given) as CD ⊥ AB
OD = BD | Given
∴ ∆OED ≅ ∆BED
| AAS congruence rule
∴ OE = BE | C.P.C.T.
Now, in ∆CEO and ∆CEB,
CE = CE | Common
∠CEO = ∠CEB | Each = 90°
OE = BE | Proved above
∴ ∆CEO ≅ ∆CEB
| SAS congruence rule
∴ CO = CB ...(1)
∠ACB = 90°
| Angle in a semi-circle is a right angle
∴ OA = OB = OC ...(2)
| ∵ The mid-point of the hypotenure of a right angled triangle is equidistant from its vertices
From (1) and (2),
OB = OC = BC
∴ ∆OBC is equilateral
∴ ∠BOC = 60°
| Each angle of an equilateral triangle is 60°
⇒ 2 ∠BAC = 60°
| The angle subtended by an arc of a circle at the centre is twice the angle subtended by it at any point on the remaining part of the circle
⇒ ∠BAC = 30°
⇒ ∠CAB = 30°.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type5. In the given figure, find the values of a, b, c and d. Given that ∠BCD = 43° and ∠BAE = 62°.