 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type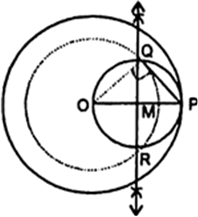
Steps of Construction :
(i) Join PO and bisect it. Let M be the midpoint of PO.
(ii) Taking Mas centre and MO as radius, draw a circle. Let it intersect the given circle at the point Q and R.
(iii) Join PQ.
By measurement PQ = 4.5 cm
Then PQ is the required tangent.
By actual calculation,
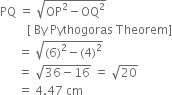
Justification :
Join OQ. Then ∠PQO an angle in the semi-circle and, therefore
∠PQO = 90
⇒ PQ ⊥ OQ
Since, OQ is a radius of the given circle, PQ has to be a tangent to the circle.
