 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeSteps of Construction :
(i) Bisect PQ. Let M be the mid-point of PO.
(ii) Taking M as centre and MO as radius, draw a circle which intersect the given circle at the points A and B.
(iii) Join PA and PB.
Now, PA and PB are the required two tangents.
(iv) Bisect QO. Let N be the mid-point of QO.
(v) Taking N as centre and NO as radius, draw a circle. Let it intersect the given circle at the points C and D.
(vi) Join QC and QD.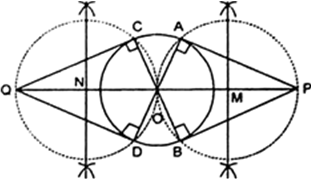
Then QC and QD are the required two tangents.
Justification : Join OA and OB.
Then ∠PAO is an angle in the semicircle and, therefore,
∠PAO = 90°
⇒ PA ⊥ OA
Since, OA is a radius of the given circle, PA has to be a tangent to the circle. Similarly, PB is also a tangent to the circle.
Again, Join OC and OD.
Then ∠QCO is an angle on the semicircle and therefore,
∠QCO = 90°
Since, OC is a radius of the given circle, QC has to be a tangent to the circle.
Similarly, QD is also a tangent to the circle.
