 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsIf a curve y=f(x) passes through the point (1, −1) and satisfies the differential equation, y(1+xy) dx=x dy, then f(-1/2) is equal to
-2/5
-4/5
2/5
2/5
If f and ga re differentiable functions in (0,1) satisfying f(0) =2= g(1), g(0) = 0 and f(1) = 6, then for some c ε] 0,1[
2f'(c) = g'(c)
2f'(c) = 3g'(c)
f'(c) = g'(c)
f'(c) = g'(c)
The population p(t) at time t of a certain mouse species satisfies the differential equation 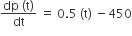 . if p (0) = 850, then the time at which the population becomes zero is
. if p (0) = 850, then the time at which the population becomes zero is
2 log 18
log 9
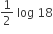
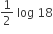
Consider the function f(x) = |x – 2| + |x – 5|, x ∈ R.
Statement 1: f′(4) = 0
Statement 2: f is continuous in [2, 5], differentiable in (2, 5) and f(2) = f(5).
Statement 1 is false, statement 2 is true
Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is true; statement 2 is a correct explanation for statement 1
Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is true; statement 2 is not a correct explanation for statement 1
Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is true; statement 2 is not a correct explanation for statement 1
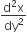 equal to
equal to
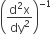
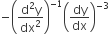
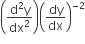
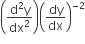
D.
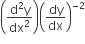
The shortest distance between line y - x = 1 and curve x = y2 is
√3/4
3√2 /8
8/3√2
8/3√2
Let f : R → R be a continuous function defined
by f(x) = 1/ex + 2e-x
Statement - 1: f(c) = 1/3, for some c ∈ R.
Statement-2: 0 < f(x)≤  , for all x ∈ R.
, for all x ∈ R.
Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is true; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1.
Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is true; statement-2 is not a correct explanation for Statement-1.
Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is false.
Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is false.
The equation of the tangent to the curve , that is parallel to the x-axis, is
, that is parallel to the x-axis, is
y = 0
y = 1
y = 3
y = 3
