 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeYou have studied in Class IX, (Chapter 9, Example 3), that a median of a triangle divides it into two triangles of equal areas. Verify this result for Δ ABC whose vertices are A(4, – 6), B(3, –2) and C(5, 2)
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeDetermine the ratio in which the line 2x + y – 4 = 0 divides the line segment joining the points A(2, – 2) and B(3, 7).
Find the centre of a circle passing through the points (6, – 6), (3, – 7) and (3, 3).
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeThe two opposite vertices of a square are (–1, 2) and (3, 2). Find the coordinates of the other two vertices.
The Class X students of a secondary school in Krishinagar have been allotted a rectangular plot of land for their gardening activity. Sapling of Gulmohar are planted on the boundary at a distance of 1m from each other. There is a triangular grassy lawn in the plot as shown in the Fig. 7.14. The students are to sow seeds of flowering plants on the remaining area of the plot.
(i) Taking A as origin, find the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle.
(ii) What will be the coordinates of the vertices of Δ PQR if C is the origin?
Also calculate the areas of the triangles in these cases. What do you observe?
The vertices of a Δ ABC are A(4, 6), B(1, 5) and C(7, 2). A line is drawn to intersect sides
AB and AC at D and E respectively, such that ![]() Calculate the area of the ∆ADE and compare it with the area of ∆ABC.
Calculate the area of the ∆ADE and compare it with the area of ∆ABC.

⇒ D and E divide AB and Ac respectively in the ratio 1 : 3.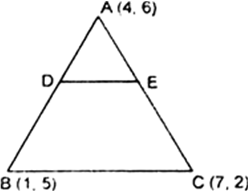
So, the co-ordinates of D and E are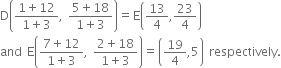
Now,
∴ Area of ∆ADE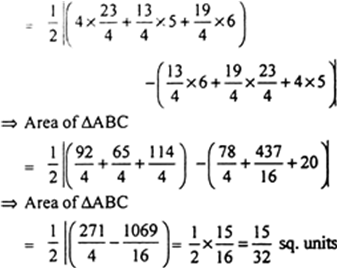
And
∴ Area of ∆ABC
Hence, Area of ∆ABC = 1 : 16.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeLet A (4, 2), B(6, 5) and C(1, 4) be the vertices of Δ ABC.
The median from A meets BC at D. Find the coordinates of the point D.
Let A (4, 2), B(6, 5) and C(1, 4) be the vertices of Δ ABC.
Find the coordinates of the point P on AD such that AP : PD = 2 : 1
Let A (4, 2), B(6, 5) and C(1, 4) be the vertices of Δ ABC.
Find the coordinates of points Q and R on medians BE and CF respectively such that BQ : QE = 2 : 1 and CR : RF = 2 : 1.
