 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeHere, ![]() ...(1)
...(1)
Differentiating w.r.t.x, we get,
![]()
![]() ...(2)
...(2)
Dividing (2) by (1), we get.
![]()
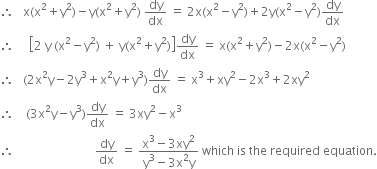
Hence the result.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type