 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeObtain the differential equation from the equation y = ex (a cos 2x + b sin 2x). where a and b are arbitrary constants.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeLet the radius of circle = a
Since the circle has centre on x-axis and passes through the origin.
∴ its centre is (a, 0)
The equation of circle is
( x – a)2+( y – 0)2 = a2 or x2 –2 a x + a2 + y2 = a2
∴ x2 + y2 – 2 ax = 0 ...(1)
Differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get.
![]()
![]()
Putting this value of a in (1), we get.
![]()
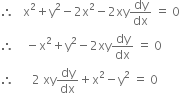
which is required differential equation.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type