 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeLet C denote the family of circles touching x-axis at origin. Let (0, a) be the coordinates of the centre of any member of the family where ‘a’ is an arbitrary constant.
∴ the equation of family C is
x2 + (y – a)2 = a2
∴ x2 + y2 + a2 – 2 a y = a2
or x2 + y2 – 2 a y = 0 ...(1)
a being arbitrary constant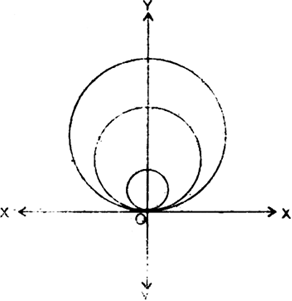
Differentiating w.r.t. x, we get
![]()
![]()
![]() ...(2)
...(2)
[Multiplying by y]
Multiplying (1) by ![]()
![]() ...(3)
...(3)
Subtracting (3) from (2), we get,
![]()
or ![]() or
or ![]()
which is required differential equation.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type