 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeSolve the following problem graphically:
Minimise and Maximise Z = 3x + 9y
subject to the constraints:
x + 3y ≤ 60
x + y ≥ 10
x ≤ y
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Solve the following linear programming problem graphically:
Minimise Z = 3x + 5y subject to the constraints:x + 3y ≥ 3, x + y ≥ 2, x, y ≥ 0
We are to minimise, Z = 3x + 5y subject to the constraints x + 3y ≥ 3, x + y ≥ 2, x, y ≥ 0
Consider a set of rectangular cartesian axes OXY in the plane.
It is clear that any point which satisfies x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 lies in the first quadrant.
Let us draw the graph of x + 3y = 3
For x = 0, 3 y = 3 or y = 1
For y = 0, x = 3
∴ line meets OX in A(3, 0) and OY in L(0, 1).
Again we draw the graph of x + y = 2
For x = 0, y = 2
For y = 0, x = 2
∴ line meets OX in B(2, 0) and OY in M(0, 2).
Since feasible region is the region which satisfies all the constraints.
∴ shaded region is the feasible region which is unbounded and has comer points
![]()
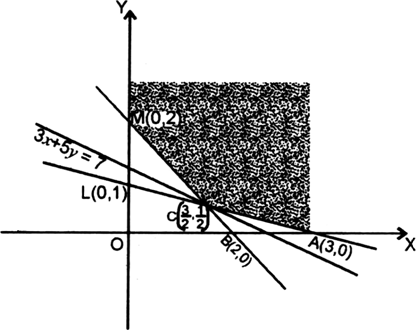
Since feasible region is unbounded.
∴ we are to check whether this value is minimum.
For this we draw the graph of
3x + 5y < 7 ...(1)
Since (1) has n.o common point with feasible region.![]()
