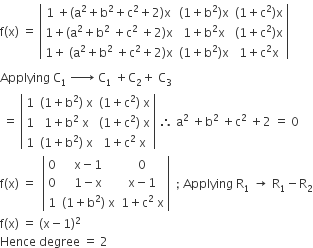Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsLet A and B be two symmetric matrices of order 3.
Statement-1: A(BA) and (AB)A are symmetric matrices.
Statement-2: AB is symmetric matrix if matrix multiplication of A with B is commutative.
Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is true; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1.
Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is true; Statement-2 is true; Statement-2 is not a correct explanation for Statement-1.
Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is false.
Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is false.
The number of 3 × 3 non-singular matrices, with four entries as 1 and all other entries as 0, is
less than 4
5
6
6
Let f : R → R be defined by 
If f has a local minimum at x = - 1 then a possible value of k is
1
0
-1/2
-1/2
If S is the set of distinct values of 'b' for which the following system of linear equations
x + y + z = 1
x + ay + z = 1
ax + by + z = 0
has no solution, then S is
a singleton
an empty set
an infinite set
an infinite set
Let ω be a complex number such that 2ω +1 = z where z = √-3. if
then k is equal to
1
-z
z
z
Let a, b, c be such that 0 (a +c) ≠ . If  ,then the value of 'n' is
,then the value of 'n' is
0
any even integer
any odd integer
any odd integer
Let A be a 2 × 2 matrix
Statement 1 : adj (adj A) = A
Statement 2 : |adj A| = |A|
Statement–1 is true, Statement–2 is true, Statement–2 is a correct explanation for statement–1
Statement–1 is true, Statement–2 is true; Statement–2 is not a correct explanation for statement–1.
Statement–1 is true, statement–2 is false.
Statement–1 is true, statement–2 is false.
If A and B are square matrices of size n × n such that A2 − B2 = (A − B) (A + B), then which of the following will be always true?
A = B
AB = BA
either of A or B is a zero matrix
either of A or B is a zero matrix
If a2 + b2 + c2 = -2 and  then f(x) is a polynomial of degree
then f(x) is a polynomial of degree
1
0
2
2
C.
2