 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeLet the first child be denoted by capital letter and the second i.e. younger one by a smaller letter.
Ōł┤ ┬ĀS = {Bb, Bg, Gb, Gg}
Let E : both children are girls
Ōł┤ E = {Gg}
Let F : at least one is a girl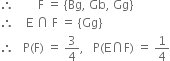
Required probability =┬Ā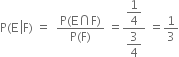
A family has two children. What is the probability that both the children are boys given that at least one of them is a boy?
A couple has two children,
Find the probability that both children are males, if it is known that at least one of the children is male.┬Ā
A couple has two children,
Find the probability that both children are females, if it is known that the elder child is a female.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeAn electronic assembly consists of two subsystems, say A and B. From the previous testing procedures, the following probabilities are assumed to be known:
P( A fails) = 0.2
P(B fails alone) = 0.15
P(A and B fail) = 0.15
Evaluate the following probabilities:
(i) P( A fails┬Ā![]() ) (ii) P(A fails alone)
) (ii) P(A fails alone)
 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice Questions