 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeLet A be the event that the machine produces 2 acceptable items.
Again, let B1 represent the event of correct setup and B2 represent the event of incorrect setup.
Now, ![]()
![]()
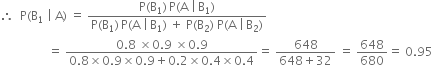
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeSuppose that the reliability of HIV test is specified as follows:
Of people having HIV, 90% of the test detect the disease but 10% go undetected. Of people free of HIV, 99% of the test are judged HIV -ve but 1% are diagonsed as showing HIV +ve. From a large population of which only 0.1% have HIV, one person is selected at random, given the HIV test, and the pathologist reports him/her as HIV +ve. What is the probability that the person actually has HIV?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type