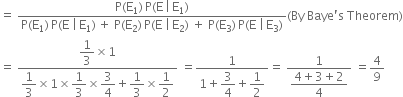Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeSuppose that the reliability of HIV test is specified as follows:
Of people having HIV, 90% of the test detect the disease but 10% go undetected. Of people free of HIV, 99% of the test are judged HIV -ve but 1% are diagonsed as showing HIV +ve. From a large population of which only 0.1% have HIV, one person is selected at random, given the HIV test, and the pathologist reports him/her as HIV +ve. What is the probability that the person actually has HIV?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeLet E1, E2, E3, E be the events
E1 : ‘coin chosen is two headed’,
E2 : ‘coin chosen is biased’,
E3 : ‘coin chosen is unbiased’,
E : ‘tossed coin shows up a head’
![]()
![]()
Required probability = ![]()