Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeGiven: ABCD is a quadrilateral whose diagonals AC and BD intersect each other at right angles at O.
To Prove: Quadrilateral ABCD is a rhombus.

Proof: In ∆AOB and ∆AOD,
AO = AO | Common
OB = OD | Given
∠AOB = ∠AOD | Each = 90°
∴ ∆AOB ≅ ∆AOD
| SSS Congruence Rule
∴ AB = AD ...(1) | C.P.C.T.
Similarly, we can prove that
AB = BC ...(2)
BC = CD ...(3)
CD = AD ...(4)
In view of (1), (2), (3) and (4), we obtain
AB = BC = CD = DA
∴ Quadrilateral ABCD is a rhombus.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeDiagonal AC of a parallelogram ABCD bisects ∠A (see figure). Show that:
(i) it bisects ∠C also
(ii) ABCD is a rhombus.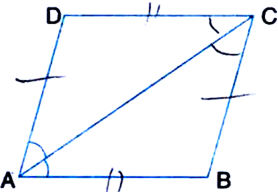
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type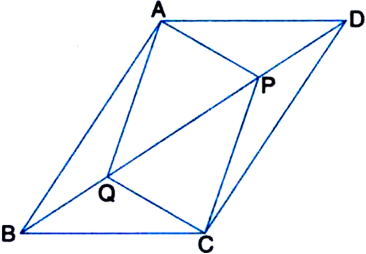
(i) ∆APD ≅ ∆CQB
(ii) AP = CQ
(iii) ∆AQB ≅ ∆CPD
(iv) AQ = CP
(v) APCQ is a parallelogram.
 Short Answer Type
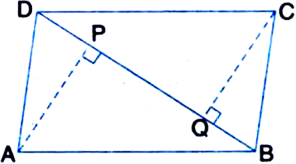
Short Answer TypeABCD is a parallelogram and AP and CQ are perpendiculars from vertices A and C on diagonal BD respectively (see figure). Show that:
(i) ∆APB ≅ ∆CQD
(ii) AP = CQ.