 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeIf the function f: R  R be given by
R be given by  be given by
be given by  find fog and gof and hence find fog (2) and gof ( −3).
find fog and gof and hence find fog (2) and gof ( −3).
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeDiscuss the commutativity and associativity of binary operation '*' defined on A = Q − {1} by the rule a * b = a − b + ab for all, a, b ∊ A. Also find the identity element of * in A and hence find the invertible elements of A.
Consider f : R+ → [−5, ∞), given by f(x) = 9x2 + 6x − 5. Show that f is invertible with f−1(y) .
.
Hence Find
(i) f−1(10)
(ii) y if f−1(y)=43,
where R+ is the set of all non-negative real numbers.
f : R+ → [−5, ∞) given by f(x) = 9x2+ 6x − 5
To show: f is one-one and onto.
Let us assume that f is not one-one.
Therefore there exist two or more numbers for which images are same.
For x1, x2∈ R+ and x1≠ x2
Let f(x1)=f(x2)
⇒9x12+6x1−5=9x22+6x2−5
⇒9x12+6x1=9x22+6x2
⇒9x12−9x22+6x1−6x2=0
⇒9(x12−x22)+6(x1−x2)=0
⇒(x1−x2)[9(x1+x2)+6]=0
Since x1 and x2 are positive,
9(x1+x2)+6>0
∴x1−x2=0
⇒x1=x2
Therefore, it contradicts our assumption.
Hence the function f is one-one.
Now, let is prove that f is onto.
A function f : X → Y is onto if for every y ∈ Y, there exist a pre-image in X.
f(x)=9x2+6x−5
=9x2+6x+1−6
=(3x+1)2−6
Now, for all x∈R+ or [0,∞), f(x)∈[−5, ∞).
∴ Range = co-domain.
Hence, f is onto.
Therefore, function f is invertible.
Now, let y = 9x2 + 6x − 5
9x2+6x−5−y=0
or
9x2+6x−(5+y)=0 where x∈R+
As x∈R+ i.e., is a positive real number
x cannot be equal to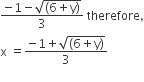
Since f: R+ →[-5,∞)
so y ∈ [-5,∞)
i.e y is greater than or equal to -5
i.e. y ≥-5
y+5 ≥0
⇒ Hence the value inside root is positive
Hence √y +6≥0
⇒ x≥0
Hence x is a real number which is greater than or equal to 0.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeIf a*b denotes the larger of 'a' and 'b' and if a o b = (a*b) + 3, then write the value of (5) o (10), where and o are binary operations.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeLet A = { x ∈ Z: 0 ≤ x≤ 12} show that R = {(a,b):a,b ∈ A, |a-b|} is divisible by 4} is an equivalence relation. Find the set of all elements related to 1. Also, write the equivalence class [2].
Show that the function f: R → R defined by si neither one- one nor onto. Also, if g: R → R is defined as g(x) = 2x -1 find fog (x)
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(i) Is the binary operation *, defined on set N, given by a * b = for all a,b N, commutative?
(ii) Is the above binary operation * associative?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeIf the binary operation * on the set of integers Z, is defined by a * b = a + 3b2 , then find the value of 2 * 4.
