 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Typeet AB be the surface of the lake and 'P' be the position of the observer h metres above the lake. Let C be the cloud and C' be the reflection in the cloud. Then CB = C'B. It is also given that the angle of elevation of cloud from a point h m above a lake is α and angle of depression of its reflection be β. i.e., ∠CPQ = α and ∠QPC' = β. Let CQ = xm.
In right triangle PQC, we have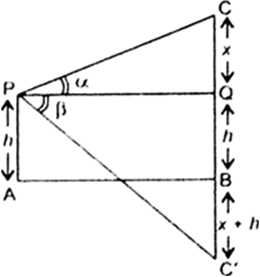
In right triangle PQC, we have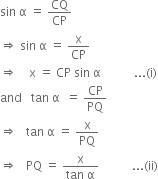
In right triangle PQC', we have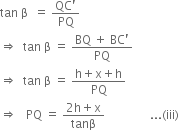
Comparing (ii) and (iii), we get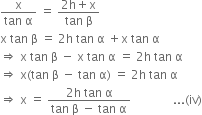
Comparing (i) and (iv), we get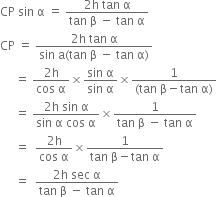
Hence, the distance of the cloud from the point of observer is ![]()
