 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeLet D be the vertical position of the aeroplane of height h mile i.e., CD = h miles. Let A and B are the position of two stones on opposite sides of the aeroplane which are at a distances of 1 mile from each other. It is also given that the angles of depression of these stones from the aeroplane are α and β respectively.
i.e., ∠CAD = α and ∠CBD = β
Let AC = x then BC = 1-x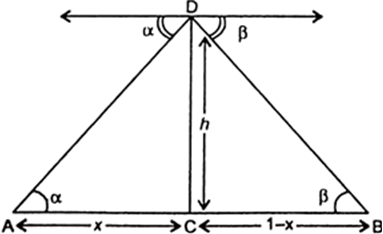
In right triangle ACD, we have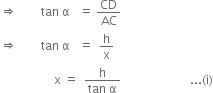
In right triangle BCD, we have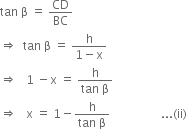
Comparing (i) and (ii), we get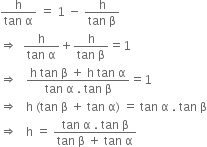
Hence, the height of the aeroplane above the road in miles be ![]() .
.
