 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeFind the projection of the line segment joining the points (1, 2, 3), (4, 3, 1) on the line with direction ratios 3, –6, –2.
A directed line segment makes angles 45° and 60° with x-axis and y-axis and an acute angle with z-axis. If P (– 1, 2, – 3) and Q (4, 3, 1) are two points in space, find the projection of PQ on the given line.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type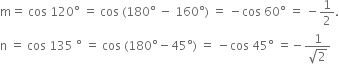
If P, Q, R, S are the points (– 2, 3, 4), (– 4, 4, 6), (4, 3, 5), (0, 1, 2), prove by projection that PQ is perpendicular to RS.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeThe projections of a directed line segment on the co-ordinate axes are 6, -3, 2. Find its length and direction cosines.
