 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type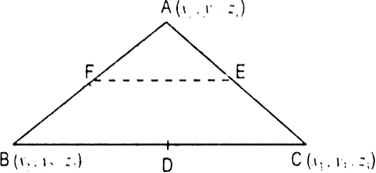
Direction-ratios of BC are
x3¬†‚Äď x2, y3¬†‚Äď y2, z3¬†‚Äď z2.
Directions-ratios of FE are
          ![]()
or        ![]()
or      ![]()
which are the same as that of BC
‚ąī ¬† ¬†FE || BC.
Also,
 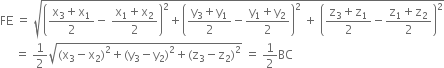
Hence the result. 
Find the angle between the two lines whose direction cosines are given by the equations:
l + m + n = 0, ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† l2¬†+ m2¬†‚Äď n2¬†= 0
