 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeThe equation of any plane through (– 1,–1, 2) is
a(x + 1) + b(y + 1) + c(z – 2) = 0 ...(1)
∴ it is perpendicular to the planes
2x + 3y – 3z = 2 and 5x – 4y + z = 6
∴ 2a + 3b – 3c = 0 ...(2)
and 5a – 4b + c = 0 ...(3)
Solving (2) and (3), we get,
![]()
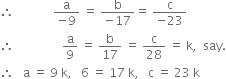
∴ a = 9 k, 6 = 17 k, c = 23 k
Putting values of a, b, c in (1), we get
9 k (x + 1)+ 17 k (y + 1) + 23 k (z – 2) = 0
or 9 (x + 1) + 17 (+ 1) + 23 (z – 2) = 0
or 9 x + 9 + 17 y + 17 + 23 z – 46 = 0
or 9 x + 17 y + 23 z – 20 = 0
which is required equation of plane.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type