 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type
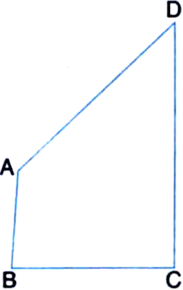
Given: AB and CD are respectively the smallest and longest sides of a quadrilateral ABCD.
To Prove: ∠A > ∠C and ∠B > ∠D
Construction: Join AC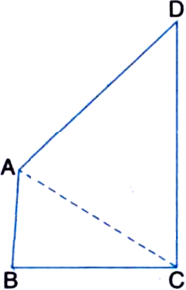
Proof: In ∆ABC,
AB < BC
| ∵ AB is the smallest side of quadrilateral ABCD
⇒ BC > AB
∴ ∠BAC > ∠BCA ...(1)
| Angle opposite to longer side is greater In ∆ACD,
CD > AD
| ∴ CD is the longest side of quadrilateral ABCD
∴ ∠CAD > ∠ACD ...(2)
| Angle opposite to longer side is greater
From (1) and (2), we obtain
∠BAC + ∠CAD > ∠BCA + ∠ACD
⇒ ∠A > ∠C
Similarly, joining B to D, we can prove that ∠B > ∠D.
[Hint. Produce AD to E such that AD = DE and join C and E.]
OR
Prove that the sum of any two sides of a triangle is greater than twice the length of median drawn to the third side.
Prove that the sum of the three sides of a triangle is greater than the sum of its three medians.
OR
Prove that the perimeter of a triangle is greater than the sum of its three medians.
