 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice Questions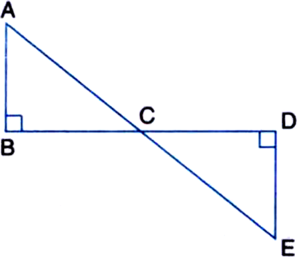
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeShow that ΔABC, where A(–2, 0), B(2, 0), C(0, 2) and ΔPQR where P(–4, 0), Q(4, 0), R(0, 2) are similar triangles.
In ΔABC, the coordinates of the vertices are A(–2, 0), B(2, 0), C(0, 2).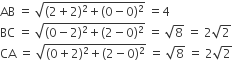
In ΔPQR, the coordinates of the vertices are P(–4, 0), Q(4, 0), R(0, 4).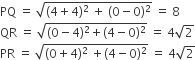
Now, for ΔABC and ΔPQR to be similar, the corresponding sides should be proportional.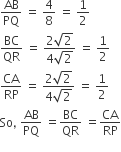
Thus, ΔABC is similar to ΔPQR.
Prove that the area of an equilateral triangle described on one side of the square is equal to half the area of the equilateral triangle described on one of its diagonal.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeProve that, in a right triangle, the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sides.
 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsABCD is a rectangle whose three vertices are B (4, 0), C(4,3) and D(0, 3). The length of one of its diagonals is
5
4
3
25
