 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type
Given: In quadrilateral ACBD, AC = AD and AB bisects ‚ą†A.
To Prove: ‚ąÜABC ‚ČÖ ‚ąÜABD.
Proof: In ‚ąÜABC and ‚ąÜABD,
AC = AD    | Given
AB = AB    | Common
‚ą†CAB = ‚ą†DAB
| ‚ąĶ AB bisects ‚ą†A
‚ąī ‚ą†ABC ‚ČÖ ‚ą†ABD ¬†¬†¬†| SAS Rule
‚ąī BC = BD ¬†¬†¬†| C.P.C.T,

(i) ‚ąÜABD ‚ČÖ ‚ąÜBAC
(ii) BD = AC
(iii) ‚ą†ABD = ‚ą†BAC.


Line I is the bisector of an angle ‚ą†A and B is any point on I. BP and BQ are perpendiculars from B to the arms of ‚ą†A (see figure). Show that:
(i) ‚ąÜAPB ‚ČÖ ‚ąÜAQB
(ii) BP = BQ or B is equidistant from the arms of ‚ą†A.
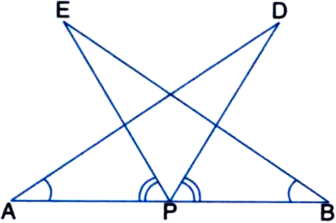
(i) ‚ąÜDAP ‚ČÖ ‚ąÜEBP
(ii) AD = BE.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type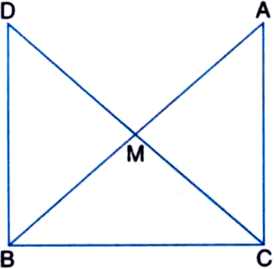
(i) ¬†¬†¬†‚ąÜAMC ‚ČÖ ‚ąÜBMD
(ii) ¬†¬†¬†‚ą†DBC is a right angle
(iii) ¬†¬†¬†‚ąÜDBC ‚ČÖ ‚ąÜACB![]()
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type
