Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type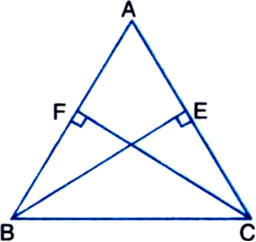
(i) ∆ABE ≅ ∆ACF
(ii) AB = AC, i.e., ∆ABC is an isosceles triangle.
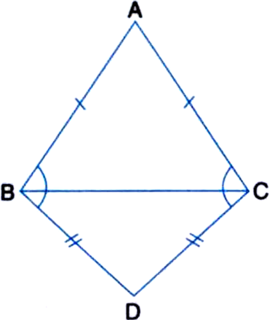
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type∆ABC is an isosceles triangle in which AB = AC. Side BA is produced to D such that AD = AB (see figure). Show that ∆BCD is a right angle.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type∵ In ∆ABC,
AB = AC
∴ ∠B = ∠C ...(1)
| Angles opposite to equal sides of a triangle are equal
In ∆ABC,
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180°
| Sum of all the angles of a triangle is 180°
⇒ 90° + ∠B + ∠C = 180°
| ∵ ∠A = 90° (given)
⇒ ∠B + ∠C = 90° ...(2)
From (1) and (2), we get
∠B = ∠C = 45°.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeABC is a triangle in which ∠B = 2∠C. D is a point on side BC such that AD bisects ∠BAC and AB = CD. Prove that ∠BAC = 72°.
[Hint. Take a point P on AC such that BP bisects ∠B. Join P and D.]
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type