 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsA pharmacy student designed a drug to specifically target the receptors for retinoic acid in order to prevent stem cell differentiation. After in vitro trial, the investigators found that the cells underwent differentiation and the drug seemed to be ineffective. The following reasons were given by the student.
A. The size of the drug exceeded the size of molecules that could cross the membrane.
B. The drug was small in size but hydrophobic in nature.
C. The drug did not bind to its receptors.
Which of the above could be the probable reason for drug ineffectiveness?
Only C
A and C
A, B and C
Only B
A researcher wanted to immunize individuals of a particular area with viral infections. The researcher developed two different vaccine types (A and B) with the following properties.
(i) When vaccine type A specific for a viral strain is administered to individuals, they develop strong neutralizing antibody response with very poor immunological memory. Hence it has to be administered in repetitive doses.
(ii) When vaccine type B specific for a viral strain is administered to individuals, they fail to develop circulating antibody response at the time of infection but they develop strong immunological memory.
If two viral strains V1 (incubation period-2 das) and V2 (incubation period-15 days) are likely to infect the area, which of the following vaccine combination would provide maximum immunization?
V1 specific type A and V1 specific type B
V1 specific type A and V2 specific type B
V2 specific type A and V1 specific type B
V2 specific type A and V2 specific type B
For the aquaculture of Indian Major carps several techniques are used. Which one of the following techniques is NOT used for this purpose:
Induced breeding
Selective breeding
Inbreeding
Composite fish farming
The following statements are related to plant tissue culture
A. Friable callus provides the inoculum to form cell-suspension cultures.
B. The process known as 'habituation' refers to the property of callus loosing the requirement of auxin and/or cytokinin during long term culture.
C. Cellulase and pectinase enzymes are usually used for generating protoplast cultures.
D. During somatic embryo development, torpedo stage embryo is formed before heart stage embryo.
Which one of the following combinations of above statements is correct?
A, B and C
A, B and D
A, C and D
B, C and D
The nodulation (nod) genes are classified as common nod genes or host specific nod genes. Some statements related to such classification are given below:
A. nodA is a common nod gene and nodC is a host specific gene.
B. nodB is a common nod gene and nodP is a host specific gene.
C. nodQ is a common nod gene and nodA is a host-specific gene.
D. nodH is a common nod gene and nodQ is a host-specific gene.
Choose the correct answer from the above statements:
A and B
C and D
A only
B only
D.
B only
Among the given set of statements, nodB is a common nod gene and nodP is a host specific gene is the correct statement.
Application of gene therapy in clinical trails did not succeed due to
poor integration of a gene in the host genome.
lack of expression of an integrated gene in cells.
degradation of genes inside the cell.
activation of oncogenes consequent to the integration of the gene.
Molecular polmorphic markers are already known with respect to tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) resistance in tobacco. Among these, which marker system you will select that will be simple, economic and less time consuming:
RAPD
RFLP
AFLP
EST-SSR
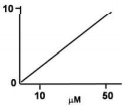
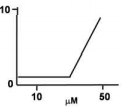
Performance of biosensor is evaluated by their response to the presence of an analyte. The physiological relevant concentration of analyte is between 10μM and 50μM. Which among the following biosensor responses is best?


TILLING is a reverse genetics approach used in functional genomics. Which one of the following is used for TILLING?
T-DNA tagging by Agrobacterium-mediated transformation.
Transposon tagging used Ac/ Ds elements
Mutagenesis with ethylmethane sulphonate.
Protoplast transformation by electroporation
Which one of the following is a foodborne toxin?
Tetanus toxin
Botulinum toxin
Cholera toxin
Diptheria toxin
