 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsEntry of enveloped viruses into its host cells is mediated by:
Only endocytosis
both endocytosis and phagocytosis
both endocytosis and membrane fusion
only pinocytosis
Mitotic cyclin-CDK activity peaks in the M phase. This is because
Mitotic cyclin is synthesized only in M phase.
The threshold level of mitotic cyclin accumulates only in late G2.
Cyclin subunit is activated by phoshorylation only in M phase.
The kinase subunit is activated by dephosphorylation only in M phase.
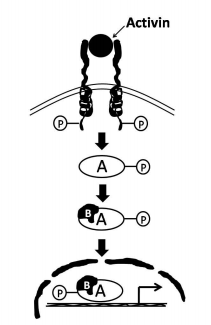
In the above signalling cascade, which one of the following molecules is denoted by 'B'?
STAT 5
SMAD 6
GSK3β
SMAD 4
The secondary antibodies routinely used for the detection of primary antibodies in western blotting experiment are
anti-allotypic
anti-idiotypic
anti-isotypic
anti-paratypic
Which of the following events will NOT usually lead to the transformation of a normal cell into a cancer cell?
Gain of function of oncogenes.
Loss of function of tumor suppressors.
Gain of function of genes involved in nucleotide excision repair.
Loss of function of pro-apoptosis related genes.
C.
Gain of function of genes involved in nucleotide excision repair.
Gain of function of genes involved in nucleotide excision repair will not lead to transformation of a normal cell into a cancer cell.
Cell to cell communication is important in the development of an organism. The ability of a cell to respond to a specific inductive signal is called
Regional specificity of induction
Competence
Juxtacrine signalling
Instructive interaction
Which one of the following does NOT occur due to stimulation of baroreceptors?
Bradycardia
Hypotension
Venodilation
Vasoconstriction
In order to study the intracellular trafficking of protein 'A", it was tagged with GFP (A-GFP). Fluorescence microscopy showed that A-GFP co-localizes with LAMP1. In the presence of bafilomycin A, an inhibitor of H+-ATPase, A-GFP does not co-localize with LAMP1. Instead, it co-localizes with LC3 puncta.
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A-GFP targets to the ER in the absence f bafilomycin A.
Autophagy is required for trafficking of A-GFP to lysosomes.
Bafilomycin A facilitates targeting of A-GFP to the ER.
Bafilomycin A facilitates targeting of A-GFP to the mitochondria.
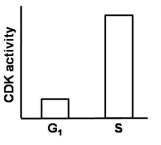
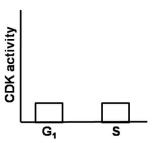
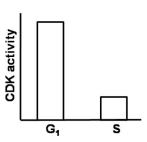
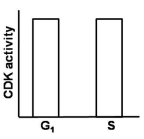
In eukaryotes, a specific cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) activity is required for the activation of loaded helicase to initiate replication. On the contrary, this CDK activity inhibits the loading of helicases onto the origin of replication. Considering the fact that during each cycle, there is only one opportunity for helicases to be loaded onto origins and only one opportunity for these loaded helicases to be activated, which one of the following graphs best depicts this CDK activity in G1 and S phases of the cell cycle?
Following are the list of some of the pathogens (column A) and the unique mechanisms they employ for evading immune response (column B).
| A | B |
| a. Trypanosoma brucei | (i) Capable of employing unusual genetic processes by which they generate extensive variations in their surface glycoproteins (VSG). |
| b. Plasmodium falciparum | (ii) Capable of continually undergoing maturational changes in the transformation to different forms that allow that organism to change its surface molecules. |
| c. Haemophilus influenza | (iii) Capable of evading immune response by frequent antigenic changes in its hemagglutinin and neuraminidase glycoproteins. |
Which of the following is the correct match between the organism and their respective mechanisms to evade immune response?
a - (i); b - (ii); c - (iii)
a - (ii); b - (iii); c - (i)
a - (iii); b - (i); c - (ii)
a - (i); b - (iii); c - (ii)
