 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThere is evidence that following pyrogenic stimuli, cytokines produced by the CNS cause fever, possibly by local release of prostaglandins. Accordingly, the following statements have been proposed:
A. Cytokines act independently and directly on thermoregulatory centers.
B. Intrahypothalamic injection of prostaglandin receptor agonists will prevent fever.
C. Antipyretic effect of aspirin is exerted on the hypothalamus to prevent prostaglandin synthesis.
D. Aspirin blocks infections and eventually prevents fever.
Which one of the following combination of above statements is correct?
A and D
B and C
B and D
A and C
In an experiment on healthy young men, the muscarinic receptor antagonist, atropine was administered to one group (Group A) while the β-adrenergic receptor antagonist, propranolol was administered to another group (Group B) in four increasing doses of equal concentration for both the drugs. The effects of these two drugs on the heart rate are shown below:
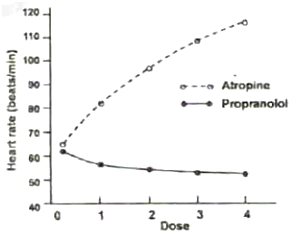
On the basis of these observations, an investigator proposed the following statements:
A. Atropine and propranolol block sympathetic and parasympathetic effects on the heart, respectively.
B. As the change of heart rate is more in Group A than in Group B, the sympathetic tone usually predominates in healthy resting individuals.
C. Atropine and propranolol block parasympathetic and sympathetic effects on the heart, respectively.
D. As substantial changes occur in the heart rate with atropine, the parasympathetic tone is predominant in healthy resting individuals.
Select the option with INCORRECT statement(s).
Only A
A and B
Only C
A and D
In kidney, Na+ is reabsorbed across the second half of proximal tubule due to positive transepithelial voltage (i.e. tubular fluid becomes positive relative to blood) and by other mechanisms. The following proposed statements could explain the development of this positive transepithelial voltage.
A. Cl- concentration gradient in the second half of the proximal tubule favours diffusion of Cl- from tubular lumen to intercellular space via a paracellular route, which generates the positive transepithelial voltage.
B. The Na+-H+ antiporters in the second half of proximal tubules create the positive transepithelial voltage.
C. The Na+-glucose symporters operating in the proximal part of renal tubules are responsible for this positive transepithelial voltage.
D. The positive transepithelial voltage is created by the operation of 1Na+-1K+-2Cl- symporter in the proximal tubules.
Select the option with correct statement(s).
Only A
B and C
C and D
Only D
Toll-like receptors (TLR) present in mammalian macrophages are recognized by types of macromolecules that are not present in vertebrates but are present in certain groups of microbial pathogens. When these pathogens infect macrophages, TLR signalling is stimulated. Following are the list of macromolecules in column A and types of TLR in column B.
| A | B |
| i. Lipopolysacharide (LPS) | a. TLR3 |
| ii. Flagellin | b. TLR4 |
| iii. Double stranded RNA | c. TLR5 |
| iv. Unmethyl CpG dinucleotides | d. TLR9 |
Which of the following is the best possible match of the pathogenic ligand with their corresponding TLR?
i - a; ii - b; iii - c; iv - d
i - b; ii - a; iii - d; iv - c
i - b; ii - c; iii - a; iv - d
i - c; ii - d; iii - b; iv - a
Preventing the blocking action of Patched protein leads to activation of Cos-2, which dissociates itself from microtubules, activates Ci/Gli which binds to CBP (CREB - binding protein) and promotes transcription of target genes. Which one of the following treatment of cells will mostly prevent Ci/Gli activated transcription in the cells?
Small molecules which target Frizzled.
Azepine, an inhibitor of γ-secretase.
Cyclopamine, which binds to heptahelical bundle of Smoothened.
Cdk blockers, which negatively regulate TGF-β induced growth.
The second messenger cAMP, synthesized by adenylyl cyclase transduces a wide variety of physiological signals in various cell types in mammalian cells. Most of the diverse effects of cAMP are mediated through activation of protein kinase A (PKA), also called cAMP dependent protein kinase. Which of the following statements regarding PKA is NOT correct?
Inactive PKA is a tetramer consisiting of two regulatory (R) subunits and two catalytic (C) subunits.
Each R subunit binds the active site in a catalytic domain and inhibits the activity of the catalytic subunits.
Each R subunit has two distinct cAMP binding sites and binding of cAMP occurs in a cooperative fashion.
Binding of cAMP to R subunit causes a conformational change resulting in binding to site other than catalytic site causing the strengthening of binding to C subunit activating its kinase activity.
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is referred to as the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) complex in humans and as the H-2 complex in mice. In an experiment, H-2k mice were primed with the lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) to induce cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) specific for the virus. Spleen cells from this LCMV-primed mouse were then added to target cells of the same (H-2b) that were intracellularly radiolabeled with 51Cr and either infected or not infected with LCMV. CTL mediated killing of target cells were then measured by the release of 51Cr into the culture supernatant (Cr release assay).
In which of the following cells, 51Cr will be released into the culture supernatant?
H-2k target cells
H-2k LCMV-infected target cells
H-2b target cells
H-2b LCMV-infected target cells
In a signalling event, binding of an extracellular ligand activates G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) that eventually activates phospholipase C-β. Which one of the following statements truly reflects the function of phospholipase C-β?
Phospholipase C-β converts PI (3, 4, 5)P3 to PI (4, 5)P2.
Phospholipase C-β converts PI (4)P to PI (4, 5)P2.
Phospholipase C-β converts PI (4, 5)P2 to diacylglycerol and IP3.
Phospholipase C-β converts PI (5) to PI (4, 5)P2.
Proteins with cytoplasmic domains having tyrosine kinase activity do NOT act as receptors for
Epidermal growth factor (EGF)
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)
Insulin
Transferrin
Which one of the following is a group of signalling molecules that act as morphogens during development of an organism and its effects are mediated through the receptor Patched and its binding partner Smoothened?
Hedgehog protein
Notch protein
Wnt protein
β-catenin
A.
Hedgehog protein
Hedgehog protein is a group of signalling molecules that act as morphogens during development of an organism and its effects are mediated through the receptor patched and its binding partner smoothened.
