 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsAn investigators expresses a GFP-fused protein that localizes to the outer membrane of golgi apparatus. Upon visualising GFP-signal in the fluorescence microscope, it was noted that GFP is pericentrosomal in its localization (fig A). Treatment of such GFP expressing cells with a newl;y identified drugs disrupted the golgi into small vesciles (fig B).
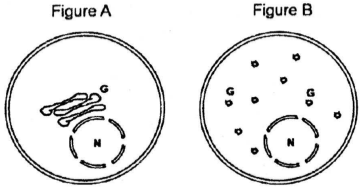
Following is a list of potential target of drugs.
Dycin complex
Myosin
Microtubules
both (a) and (c)
Following obeservation was made when a mammalian cell in one phase of cell cycle was fused with a cell in another phase of cell cycle:
(a) Fusion of cell in G1 phase with S phase caused the G1 nucleus to enter S phase.
(b) Upon fusion of a G2 cell with an S phase cell. G2 cell does not enter S phase.
(c) Upon fusion of G1 cell with G2 cell, G1 nucleus enters G2 phase.
(d) Fusion of S phase cell with a M phase causes the S phase cell to immediately enter mitosis.
Choose the combitation with all correct statements.
(a),(b),(c)
(b),(c),(d)
(a),(c),(d)
(a),(b),(d)
Bacterial chemotaxis response is mediated by histidine-kinase- associated receptors that activate a two-component signalling pathway which enables chemotaxis receptors to control the flagellar motors. When bacteria move towards attractant, they produce smooth swimming by rotating flagella counter-clockwise, whereas when bacteria move away from repellent, they produce increased tumbling by rotating flagella clockwise. Which of the following characteristics regarding chemotaxis receptor is NOT true?
The receptors are dimeric transmembrane proteins that bind specific attractants and repellents on the outside of the plasma membrane
The cytoplasmic tail of the receptor is stably associated with a histidine kinase CheA via an adapter protein CheW
The receptor and its associated proteins are all clustered at one end of the cell
The binding of an attractant increases the activity of the receptor whereas binding of repellent decrease the activity
Following are list of extracellular matrix proteins(Column A) along with their functional characteristics (Column B):
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) connexin | (i) The cheif endothelial cell proteins that are recognized by the white blood cell intergins and member of immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily |
| (b)Plasmodesmata | (ii) Cell surface carbohydrate binding proteins that mediate a variety of transient cell-cell adhension interactions in the bloodstream |
| (c) ICAM |
(iii) Four-pass transmembrane protein which is the major constituent of gap junctions in forming a continous aqueous channel
|
| (d) Selection |
(iv) It is the only class of intercellular junctions in plants that directly connects the cytoplasm of ajdacent cells |
Which one of the following is correct match?
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) |
| (i) | (iv) | (iii) | (ii) |
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) |
| (ii) | (iii) | (iv) | (i) |
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) |
| (iii) | (iv) | (i) | (ii) |
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) |
| (iv) | (i) | (ii) | (iii) |
A western blot analysis after treating cancer cells with prospective anti-cancer drug is shown below:
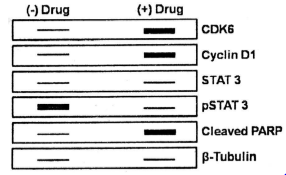
The following assumptions were made:
(a) The drug may have arrested the growth of cells at the G1 phase.
(b) The drug targeted the JAK-STAT signalling pathway.
(c) The drug led to apoptosis of the cells.
(d)Drug-induced apoptosis was through the extrinsic or mitochondrial-independent pathway.
Which of the following combination is correct?
Only (b) and (d)
Only (a), (b) and (c)
Only (a) and (b)
Only (a), (b) and (d)
Which one of the following statements regarding clonal selection hypothesis is NOT CORRECT ?
Mature B lymphocytes bear Ig receptors on their cell surface and all receptors on a single B cell have variable specificity for antigen
On antigen stimulation, B cell matures, migrates to lymphoid organns and replicates. Its clonal descendents bear the same receptor as parental B cell and secrete antibodies with identical specificity
After immune response, more B cells bearing receptors will remain in the host and act as memory cells for mounting enhanced secondary response
B cells with receptors for self antigens are deleted during embryonic development
Susceptible individuals were infected with pathogen A and pathogen B seperately. Pathogen A has a very short incubation period and disease symptoms are already underway by the time memory cells are activated. Pathogen B on the other hand has a long incubation period which allows the memory cells to be activated and respond. Which one of the following will be the most appropriate vaccination stratergy against both pathogens A and B ?
Repeated vaccination against both A and B for maintaining high levels of neutralizing antibodies
Repeated vaccination against A and a single injection of pathogen B vaccine for maintaining high levels of neutralizing antibodies
Single injection of pathogens A vaccine and repeated vaccination against pathogen B for maintaining high levels of neutralizing antibodies
Single injection of both pathogens A and B vaccine so that memory cells can respond by producing high levels of serum antibodies
B.
Repeated vaccination against A and a single injection of pathogen B vaccine for maintaining high levels of neutralizing antibodies
Memory cell production plays an important role in immunity and partly it is dependent on incubation period of the pathogen. For example, influenza virus has a very short incubation period, i.e., less than 3 days.Individuals infected with influenza readily show disease symptoms by the time immune memory cells are activated. Therefore, maintaining high levels of neutralizing antibodies in free circulation by repeated immunization is necessary for effective protection against influenza. For pathogens with a longer incubation, for example, poliovirus does not need higher levels for circulating neutralizing antibodies at the time of infection because,poliovirus requires more than 3 days to start infection of central nervous system. Due to this longer incubation period, sufficient time is provided for memory B cells to respond with production of high levels of serum antibodies.Thus, the polio vaccine is also designed to induce production of high levels of immune memory cells. If an immunized individual is later exposed to poliovirus, these memory cells will respondimmediately and within 2 weeks of time produce high levels of serum antibody, which protects the individual from infection.
Temporal expression of N-cadherin is extremely important during early development of the mammalian embroys. Accordingly, which one of the following statements about N-cadhern is true?
Injection of N-cadherin antibodies just prior to condensation of mesenchymal cells will aid cartilage formation
Presence of N-cadherin just prior to condensation will faciliate nodule formation and development of the limb skeleton
The border between the nervous system and skin will form properly only if epidermal cells are experimentally made to express N-cadherin
Expression of N-cadherin is redundant during separation of neural and epidermal precursor cells
In metazoan cell cycle, metaphase to anaphase transition is regulated by the activity of:
Cdk1/cyclinB
APC/C
Cdc25
Weel
A quadratic check of gene combinations and disease reaction types in a host-pathogen system where the gene-for-gene concept operates is represented below:
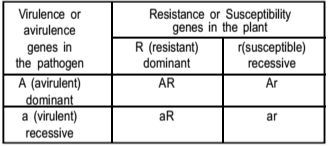
The following statements were mafde about the above genotypes:
(a) AR genotype had incompatible (resisant) reactions.
(b) Ar genotype had compatible (susceptible) reactions.
(c) ar genotype had compatible (susceptible) reactions.
(d) aR genotype had incompatible (resistant) reactions.
Choose the combination with the correct statements.
(a), (b) and (d)
(a), (b) and (c)
(b), (c) and (d)
(a), (c) and (d)
