 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsWhen a membrane is depolarized to a voltage value more positive than the threshold voltage, it leads to the generation of
Donnan potential
Action potential
Resting potential
Electrochemical potential
E. coli proliferates faster on 'glucose' than it does on 'lactose' because lactose is
taken up more slowly than glucose
not hydrolyzed by E. coli
taken up faster than glucose
toxic to the cells
Out of the list given below, which is the correct order of increasing lipid bilayer permeability?
N2 > Ethanol > H2O > Glucose > Ca+2 > RNA
H2O > Glucose > Ethanol > N2 > Ca+2 > RNA
Ca+2 > RNA > N2 > Ethanol > H2O
Ethanol > RNA > Ca+2 > H2O > Glucose > N2
Which of the following is NOT an extracellular matrix protein?
Fibronectin
Vitronectin
Laminin
Cyclin
The cylindrical channels in gap junction are made of
connexin
collagen
fibronectin
N-CAM
A.
connexin
The cylindrical channels in gap junctions are made of connexin.
When cells enter mitosis, their existing array of cytoplasmic microtubules has to be rapidly broken down and replaced with the mitotic spindle, which pulls the chromosomes into the daughter cells. The enzyme Katanin is activated during the onset of mitosis and chops microtubules into short pieces. The possible fate of the microtubule fragments created by Katapin will be
depolymerization
aggregation
degradation
translocation
A bacterial strain can use carbohydrates and hydrocarbons as growth substrates. The strain uses glucose following a minimal lag period after inoculation, regardless of the other carbohydrates and hydrocarbons in the growth medium. The following observations were also made.
A. In the absence of glucose, lactose is used after a lag period of about three times as long as the lag period for glucose utilization.
B. The presence of hydrocarbons does not affect the lag period for the utilization of lactose.
C. The utilization pattern for all hydrocarbons is similar to that of lactose.
D. Branches hydrocarbons are not immediately utilized if straight-chain hydrocarbons are initially present.
Which one of the following specific regulatory mechanisms is consistent with the above observations related to carbohydrate and hydrocarbon utilization?
Diauxie
End point repression
Catabolite repression
Transcription attenuation
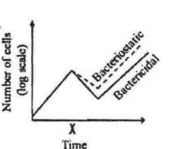
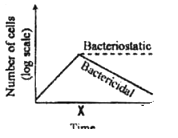
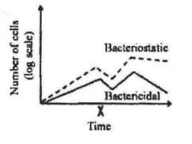
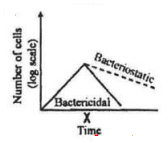
A bacterial culture was in log phase in the following figure. At time x, an antibacterial compound was added to the culture.
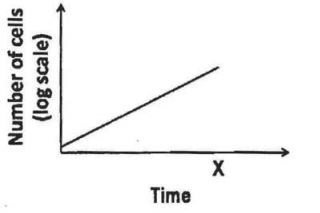
Which of the following lines in the growth curve represents the antibacterial activities of the compound?
Vascular endothelial (VE)-cadherin is an important cell adhesion molecule for endothelial cells. Endothelial cells that are unable to express VE-cadherin still can adhere to one another via N-cadherin (neural cadherin), but these cells do not survive. Which of the following is the most appropriate reason for this?
N-cadherin uses VE-cadherin as coreceptor for adhesion.
VE-cadherin acts as coreceptor for VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor)-mediated signal transduction in endothelial cells.
VE-cadherin is important for desmosome formation and interaction of intermediate filaments.
Loss of VE-cadherin impairs Ca2+- homeostasis of vascular endothelial cells leading to their death.
An action potential was generated on a nerve fiber by a threshold electrical stimulus. When a second stimulus was applied, no matter how strong it was, during the absolute refractory period of the action potential, the nerve fiber was unable to generate a second action potential. This observation was explained in the following statements:
A. A large fraction of potassium channels was voltage inactivated.
B. The critical number of sodium channels required to produce an action potential could not be recruited.
C. A large fraction of sodium channels was voltage inactivated.
D. The critical number of potassium channels required to produce an action potential could not be recruited.
Which one of the following is true?
Only A
A and B
Only C
C and D
