Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsWhich of the floral whorls is affected in agamous (ag) mutants?
Sepals and petals
Petals and stamens
Stamens and carpels
Sepals and carpels
In transverse sections of a young stem, if vallecular canals and carinal canals are present, then the plant belongs to
Lycopodiales
Isoetales
Selaginellales
Equisetales
AP1(APETLA 1) is one of the floral meristem identifying genes. In wild type Arabidopsis thaliana plants transformed with AP1::GUS, β glucuronidase (GUS) activity is seen in floral meristem, only after the commitment to flowering. Ectopic expression of AP1::GUS in the EMBRYONIC FLOWER (emf) mutant background results in GUS activity throughout the shoots in four day old seedlings. These observations suggest that AP1 is :
Not involved in flowering
Involved in repression of flowering
Involved in promoting flowering
Stimulation of flowering in the emf background
When the prospective neurons from an early gastrula of a frog were transplanted into the prospective epidermis region, the donor cells differentiated into epidermis. However, when a similar experiment was done with the late gastrula of frog, the perspective neurons developedinto neurons only. These observations could possibly be explained by the following phenomena.
A. The early gastrula show conditional development wheras the late gastrula shows autonomous development.
B. The early gastrula shows autonomous development whereas the late gastrula shows conditional development.
C. The prospective neurons from the early gastrula are only specified whereas those from the late gastrula are determined.
D. The prospective neurons from the early gastrula are determined whereas those from the late gastrula are specified.
Which of the conclusions drawn above are correct?
A and B
A and C
A and D
B and C
In case of morphallactic regeneration:
There is repatterning of the existing tissues with little new growth
There is repatterning of the existing tissues after the stem cell division has taken place
There is cell division of the differentiated cells which maintain their differentiated state to finally form a complete organism
There is dedifferentiation of the cells at the cut surface which become undifferentiated. These undifferentiated cells then divide to redifferentiate to form the complete structure
Consider the following crosses involving grey (wild type) and yellow body colour true- breeding Drosophilia:
| Cross | F1 progeny | F2 progeny | |
| Cross 1 | Grey female X yellow male |
All males : Grey All females : Grey |
Grey females : 98 Yellow males : 45 Grey ales : 49 |
| Cross 2 | Yellow females X grey males |
All males : yellow All females : grey |
? |
Assuming 200F2 offsprings are produced in cross 2, which one of the following outcomes is expected?
97 grey males, 54 yellow females, 49 grey males
102 yellow males, 46 yellow females, 52 grey females
52 grey males, 49 yellow males, 48 yellow females, 51 grey females
98 grey males, 94 yellow females, 2 yellow males, 6 grey females
With respect to development of any organism, “autonomous specification” would result in which type of development?
Regulative
Mosaic
Syncytial
Definitive
The group of cells which generates the vascular tissues including the pericycle in roots of higher plants are called
Procambium
Protoderm
Ground meristem
Apical meristem
If an embryo undergoes 13 cleavage divisions during embryogenesis, then the size of the embryo compared to zygote
Increases 13 times
Increases in an exponential fashion
Increases only 6-7 times
Remains almost the same
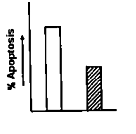
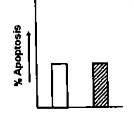
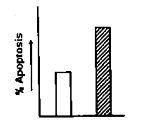
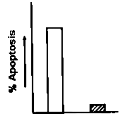
A particular type of cancer cell undergoes apoptosis by both extrinsic and intrinsic pathways when treated with a chemotherapeutic agent X. Caspase 8 and Caspase 9 are the initiator capases associated with extrinsic and intrinsic pathways respectively. Now if caspase 9 is silenced in the cancer cell by shRNA transfection, what will be the best fir graph for apoptosis scenario in the cancer cell when treated with agent X?