 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsDark-grown seedlings display 'triple response' when exposed to ethylene. Which one of the following is NOT a part of 'triple response'?
Decrease in epicotyl elongation.
Rapid unfolding and expansion of leaves.
Thickening of shoot
Horizontal growth of epicotyl.
Hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila is caused by P-elements. Which one of the following crosses between different cytotypes will lead to dysgenesis?
M-cytotype × M-cytotype
M-cytotype × P-cytotype
P-cytotype × M-cytotype
P-cytotype × P-cytotype
In eusocial insects, males develop from unfertilized eggs while females develop from fertilized eggs. The ultimate consequence of this difference is that
in any colony there are always more males than females.
a female is genetically more closely related to her sister than to her own offspring.
females are behaviourally more dominant than the males.
in any colony, there are always more females than males.
Development of vulva in C. elegans is initiated by the induction of a small number of cells by short range signals from a single inducing cell. With reference to this, following statements were put forward.
A. When the anchor cell was ablated early in development, no vulva formed.
B. In a dominant negative mutant of let-23, a primary vulva formed but the secondary vulva formation did not take place.
C. A cell adopting a primary fate inhibits adjacent cells from adopting the same fate by lateral inhibition involving LIN-39 and also induces the secondary fate in these cells.
D. A constitutive signal from the hypodermis inhibitsthe development of both the primary and secondary fates but it is overruled by the initial signal from the anchor cell.
Which of the above statements is true?
A and B
A and C
A and D
B and D
Which one of the following about the development of sea urchin embryos is TRUE?
Each blastomere of a 4-cell stage possesses a portion of the original animal-vegetal axis and if isolated and allowed to develop will form a complete but smaller sized larva.
Each blastomere of an 8-cell stage has the capacity to form a complete embryo but by the 16-cell stage, blastomeres will develop according to their presumptive fate.
Any blastomere isolated till the pluteus larva formation will regulate to go on and develop into a full sized embryo.
After an intricate recombination at the 16-cell stage, the resulting embryo loses its ability to form a complete larva
What will happen if wingless RNAi is expressed in wingless expressing cells from the stage when this gene initiates its expression in a developing Drosophila embryo?
A. The enhanced expression of wingless thus caused will broaden the area of engrailed expression.
B. Since, wingless protein makes a long range gradient, its effect will not be seen in the same segment.
C. The posterior compartment of each future segment will get affected.
D. Since engrailed expression in initiated by pair rule genes, the posterior segment will not be affected.
Which one of the following will most appropriately answer the question?
A and C
Only C
B and D
Only D
| Column A | Column B | Column C |
| (i) Invagination | (i) Movement of epithelial cells as a unit to enclose deeper layers of the embryos. | (i) Hypoblast in birds. |
| (ii) Involution | (ii) Splitting of one cellular sheet into two parallel sheets. | (ii) Ectoderm in amphibians. |
| (iii) Ingression | (iii) Infolding of epithelium | (iii) Mesoderm in amphibians |
| (iv) Delamination | (iv) Migration of individual cells from surface into interior of the embryo. | (iv) Endoderm in sea urchin. |
| (v) Epiboly | (v) Inward movement of expanding outer layer so that it spreads over the internal surface of remaining external cells. | (v) Mesoderm in sea urchin |
A - (i); B - (iv); C - (ii)
A - (iv); B - (iii); C - (i)
A - (iii); B - (iv); C - (v)
A - (v); B - (ii); C - (iii)
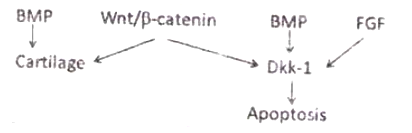
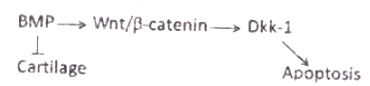
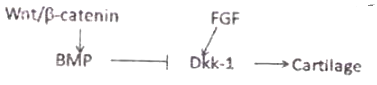
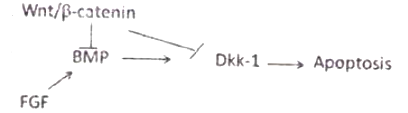
Formation of digits and sculpting the tetrapod lib requires the death of specific cells in the limb in a programmed manner. Which one of the following interactions could explain proper limb formation?
Light is an important factor for plant growth and development. there are several photoreceptors in higher plants such as Arabidopsis thaliana involved in perception of various wavelengths of light. Some statements are given below related to photoreceptors:
A. Red light photoreceptors are represented by a gene family.
B. Phytochrome C is the most prominent photoreceptor to perceive red light.
C. Cryptochrome 1 and cryptochrome 2 have evolved from bacterial DNA photolyases.
D. Far-red light is perceived by phytochrome D.
Which one of the following combinations of above statements is correct?
A and B
B and C
C and D
A and C
A student noted the following points regarding Agrobacterium tumefaciens:
A. A. tumefaciens is a gram-negative soli bacterium.
B. Opine catabolism genes are present in T-DNA region of Ti-plasmid.
C. Opines are synthesized by compensation of amino acids and α-ketoacids or amino acids and sugar.
D. A callus culture of crown gall tissue caused by A. tumefaciens in plants can be multiplied without adding phytohormone.
Which one of the combinations of above statements is correct?
A, B, and C
A, B, and D
B, C, and D
A, C, and D
