 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsMale parental care is expected to observed during:
Polygynous species
Small population size
Life long bond pairing
Reverse sexual dimorphism
One of the most important genes, involved in dorsal-ventral axis determination in Drosophila is dorsal. It codes Dorsal protein which
Is taken up into the nuclei of cells and this side will become the ventral side
remains in the cytoplasm of cell and this side will become ventral side.
Is taken up into the nuclei of cells and this side will become the dorsal side
Degraded in one side and that will become dorsal side
Which is true for amount of yolk and cleavage in egg of amphibian?
Mesolcithal and holoblastic cleavage
Isolecithal and holoblastic cleavage
Mesolecithal and meroblastic cleavage
Microlecithal and meroblastic cleavage
A.
Mesolcithal and holoblastic cleavage
Mesolecithal eggs are the eggs that have intermediate amount of yolk sac. Depending upon the amount of yolk sac, cleavage in eggs can be holoblastic which complete cleavage is or meroblastic, which is partial cleavage.
Which of the following is not a characteristic feature of Apoptosis?
Swelling of cell
Nuclear fragmentation
Change in cell wall porosity
Permeability of mitochondrial inner membrane
Cytoplasmic determinants coding for anterior structure of Drosophila embryo if injected elsewhere in the recipient embryo, would lead to
Normal development
Formation of additional ectopic head
Degeneration
A phenotype with two heads and two tails
In amphibian oocyte, the germplasm which gets segregated during cleavage to give rise to primordial germ cells (PGC’s) is normally
Distributed evenly throughout the oocyte
Localized at animal pole
Localized at vegetal pole
Aggregated in central part of oocyte
You are studying the binding of proteins to the cytoplasmic face of cultured liver cells and have found a method that gives a good yield of inside‐out vesicles from the plasma membrane. Unfortunately, your preparations are contaminated with variable amounts of right‐side‐out vesicles. Nothing you have tried avoids this contamination. Somebody suggests that you pass the vesicles over an affinity column made of lectin coupled to Sepharose beads. What is the rational of this suggestion?
Right-side-out vesicles will be lysed by lectin coupled to Sepharose beads
Right-side-out vesicles will simply bind to the lectin coupled Sepharose beads.
Lectin will bind to the carbohydrate residues present only on the inside out vesicles
Lectin will bind to only glycoproteins and glycolipids present on the inside-out-vesicles
The overall length of the cell cycle can be measured from the doubling time of a population exponentially proliferating cells. The doubling time of a population of mouse L cells was determined by counting the number of cells in samples of culture at various times. What is the overall length of the cell cycle in mouse L cells?
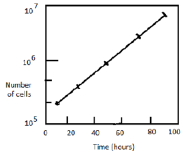
30 h
20 h
10 h
40 h
When a wrist blastema from a recently cut Axolotl forelimb is placed on a host hindlimb cut at the mid thigh level, it will generate only a wrist. The host (whose own hindlimb was removed) will fill the gap and regenerate the limb upto the wrist. However, if the donor blastema is treated with retinoic acid on grafting, the wrist blastema will regenerate a complete limb and will not allow the host to fill the gap. This happens because the retinoic acid:
Helps in the proximilization of the blastema and activates the Hox genes differentially across the blastema.
Helps in distalization of the blastema and activates the Hox genes differentially across the blastema
Helps block the receptors of FGF essential for limb development.
Helps vigorous proliferation of the cells at the cut surface.
